
Indonesia’s Economy in 2024, as measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at current market prices, reached IDR 22,139.0 trillion, with GDP per capita recorded at IDR 78.6 million or approximately USD 4,960.3.
In 2024, Indonesia’s economy grew by 5.03 percent, marking a slight slowdown compared to the 5.05 percent growth recorded in 2023 (year-on-year).
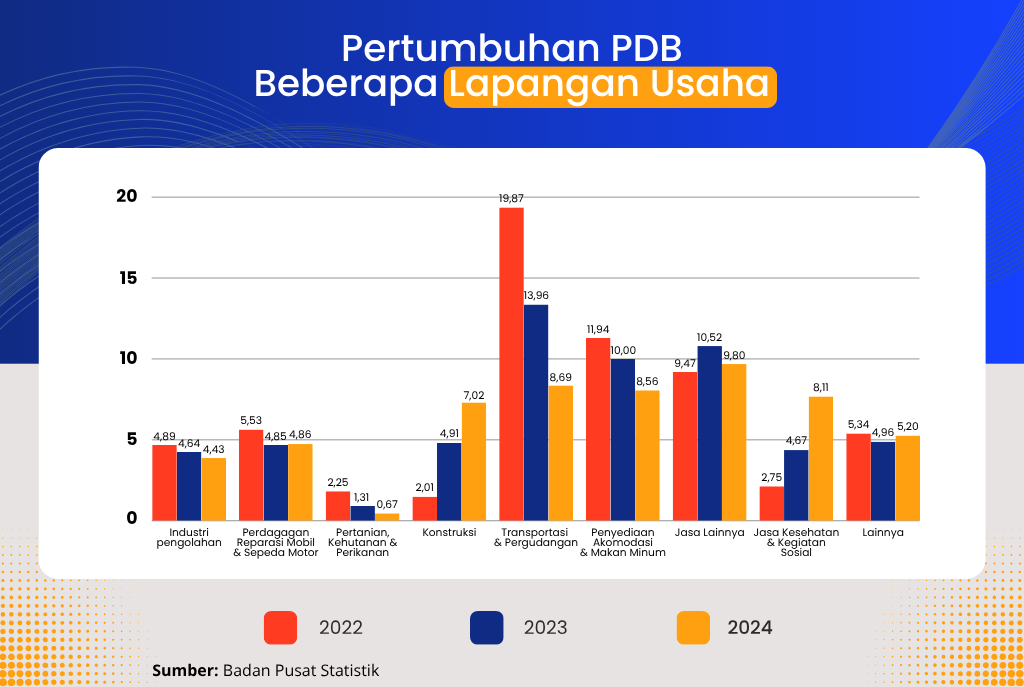
From the production side, the highest growth was recorded in the Other Services sector, which expanded by 9.80 percent, followed by Transportation and Warehousing at 8.69 percent, and Accommodation and Food & Beverage Services at 8.56 percent. Meanwhile, the Manufacturing Industry, which plays a dominant role in the economy, grew by 4.43 percent. The Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles sector, as well as the Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries sector, recorded growth rates of 4.86 percent and 0.67 percent, respectively.
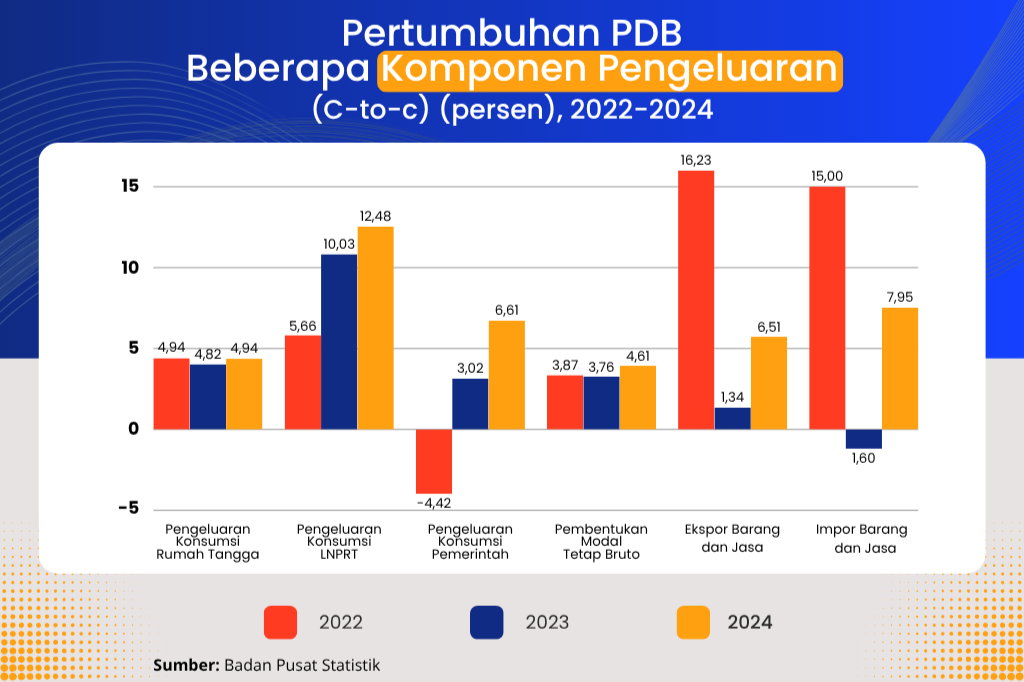
Meanwhile, from the expenditure side, the highest growth was recorded in the Consumption Expenditure Component of Nonprofit Institutions Serving Households at 12.48 percent, followed by the Government Consumption Expenditure Component at 6.61 percent; the Exports of Goods and Services Component at 6.51 percent; the Household Consumption Expenditure Component at 4.94 percent; and the Gross Fixed Capital Formation Component at 4.61 percent. Meanwhile, the Imports of Goods and Services Component (which acts as a subtractive factor in GDP based on expenditure) grew by 7.95 percent.
Indonesia’s economy in the second quarter of 2024, as measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at current market prices, reached IDR 5,536.5 trillion.


Indonesia’s economy in the second quarter of 2024 grew by 3.79 percent compared to the previous quarter (q-to-q). From the production side, the highest growth was recorded in the Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries sector, which expanded by 23.43 percent. From the expenditure side, the Government Consumption Expenditure component experienced the highest growth, at 19.58 percent.

Indonesia’s economy in the second quarter of 2024 grew by 5.05 percent compared to the second quarter of 2023 (y-on-y). From the production side, the Accommodation and Food & Beverage Services sector recorded the highest growth at 10.17 percent. Meanwhile, from the expenditure side, the Consumption Expenditure of Nonprofit Institutions Serving Households component experienced the highest growth, at 9.98 percent.
Indonesia’s economy in the first half of 2024 grew by 5.08 percent compared to the first half of 2023 (c-to-c). From the production side, the highest growth was recorded in the Public Administration, Defense, and Compulsory Social Security sector, which expanded by 10.25 percent. From the expenditure side, the Consumption Expenditure of Nonprofit Institutions Serving Households component experienced the highest growth, at 16.84 percent.

Indonesia's economy based on Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at current prices in the first quarter of 2024 reached Rp5,288.3 trillion and at constant 2010 prices Rp3,112.9 trillion.
Indonesia's economy in the first quarter of 2024 against the first quarter of 2023 grew by 5.11 percent (y-on-y).

In terms of production, the Government Administration, Defense and Compulsory Social Security Business Field experienced the highest growth of 18.88 percent. Meanwhile, in terms of expenditure, the Consumption Expenditure Component of Nonprofit Institutions Serving Households (PK-LNPRT) experienced the highest growth of 24.29 percent.

Indonesia's economy in the first quarter of 2024 against the previous quarter contracted by 0.83 percent (q-to-q). In terms of production, the deepest growth contraction occurred in the Education Services Business Field by 10.34 percent. While from the expenditure side, the Government Consumption Expenditure Component (PK-P) experienced the deepest growth contraction of 36.69 percent.

The Indonesian economy in 2023, as measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at current prices, reached Rp20,892.4 trillion and GDP per capita reached Rp75.0 million or US$4,919.7. Indonesia's economy in 2023 grew by 5.05 per cent, lower than the achievement in 2022 which experienced growth of 5.31 per cent.
Robust production activity underpins domestic economy
1. Increased Production Activity:
Bank Indonesia's Prompt Manufacturing Index (PMI) is still in the Expansion Zone reaching 51.20% higher than Quarter 4-2022 of 50.06% (source: BI)
The utilised production capacity of Quarter 4-2023 was 73.91%, higher than Quarter 4-2022 of 71.49%. (source: BI)
Cement production grew by 13.84% (y-on-y) and 3.81% (c-to-c). (source: ASI)
Electricity sales during Quarter 4-2023 grew by 9.64%, mainly driven by business segment electricity consumption which grew by 14.41% (y-on-y). (source: PLN)
2. Increased Investment Realisation:
Vehicle-type capital goods: an increase in domestic vehicle products by 12.28% and imports by 41.10% (c-to-c). (source: Gaikindo)
PMDN and PMA realisation grew 16.20% (y-on-y). (source: BKPM)
State and local government capital expenditure grew positively, strengthening compared to the previous period: 32.22% (y-on-y) and 26.31% (c-to-c). (source: APBN capital expenditure realisation)
3. Economic Policy Responses to Growth Drivers:


In terms of production, the highest growth occurred in the Transportation and Warehousing Business Field at 13.96 per cent, followed by Other Services at 10.52 per cent, and Accommodation and Drinking Food Provision at 10.01 per cent. Meanwhile, the Processing Industry, which has a dominant role, grew by 4.64 per cent. Meanwhile, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries and Wholesale and Retail Trade; Car and Motorcycle Repair grew by 1.30 per cent and 4.85 per cent respectively.
Trade grew in line with the increased supply of domestic goods:

In terms of expenditure, the highest growth was achieved by Consumption Expenditure of Nonprofit Institutions Serving Households (PK-LNPRT) by 9.83 per cent, followed by the Household Consumption Expenditure Component (PK-RT) by 4.82 per cent; Gross Fixed Capital Formation (PMTB) Component by 4.40 per cent; PK-P Component by 2.95 per cent; and the Export of Goods and Services Component by 1.32 per cent. Meanwhile, the Import Component of Goods and Services (which is a deduction factor in GDP by Expenditure) contracted by 1.65 per cent.
Quarter IV-2023 Economy

Indonesia's economy in the fourth quarter of 2023 against the fourth quarter of 2022 grew by 5.04 per cent (y-on-y). In terms of production, the Transportation and Warehousing Business Field experienced the highest growth of 10.33 per cent. While in terms of expenditure, the PK-LNPRT component experienced the highest growth of 18.11 per cent.

Indonesia's economy in the fourth quarter of 2023 against the previous quarter grew by 0.45 per cent (q-to-q). In terms of production, the Government Administration, Defence and Compulsory Social Security Business Field experienced the highest growth of 19.81 per cent. In terms of expenditure, the Government Consumption Expenditure Component (PK-P) experienced the highest growth of 39.13 per cent.
Quarter III 2023 Economy
Indonesia's economic growth in 2023 continued to improve. In the first quarter of 2023 the economy grew by 5.03% (yoy), in the second quarter of 2023 the growth was recorded at 5.17% (yoy) and in the third quarter of 2023 the growth slowed down slightly, recorded at 4.94% (yoy). In the fourth quarter of 2023, growth was estimated to be around 4.5-5.3%. The sustained domestic economic growth in the range of 5 per cent is due to the demand for domestic needs such as government and public spending that remains high.
In Q3-2023, overall exports contracted by 4.26% (yoy) due to declining demand for goods exports, in line with the global economic slowdown, deeper than the 2.97% (yoy) contraction in Q2-2023. Meanwhile, imports corrected by 6.18% (yoy) in July-September this year, deeper than the 3.06% contraction in April-June this year. This is the second time exports and imports have contracted since the fourth quarter of 2020 or the last eight quarters. However, service exports continued to grow strongly on the back of an increase in foreign tourist visits.
Indonesia's economic growth, which is currently maintained, is reflected in the Business Field and spatial aspects. By Business Field (LU), most of them in the third quarter of 2023 continued to record positive growth, mainly supported by Manufacturing Industry, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Construction. The growth of these business fields was supported by high domestic demand.
Indonesia needs foreign direct investment (FDI) to drive faster economic growth to become a developed country by 2045. Indonesia's goal for 2045 is a Nominal GDP of US$9.8 trillion with a GNI (gross national income) per capita of US$30,300 and a manufacturing contribution of 28% with a labour absorption of 25.2%.
To grow more sustainably and achieve its 2045 targets, Indonesia needs FDI due to the large saving-investment gap, which cannot be met by relying solely on the availability of domestic savings. For the 2024 growth target of 5.2 per cent, investment from various economic actors is required at around IDR 6,900 trillion.
Indonesia currently ranks 73rd in the Ease of Doing Business 2023 ranking out of 190 countries. Of the 10 assessment indicators, Indonesia's best achievement is in the ease of obtaining an electricity connection. This data is supported by the achievement of the national electrification ratio which has reached 99.72% as of June 2023. Meanwhile, Indonesia's worst assessment is on the ease of starting a business.
Indonesia's inflation in September 2023 was maintained at 2.28% (yoy) and became the lowest since February 2022. Manufacturing PMI (Purchasing Managers Index) continues to be at an expansionary level, public optimism in terms of IKK (Key Performance Indicators) is still quite high, and the Real Sales Index is still growing positively, and the Trade Balance in September 2023 is still a surplus of USD3.42 billion, continuing the surplus for 41 consecutive months.

The Indonesian economy in the third quarter of 2023 based on the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at current prices reached IDR5,296.0 trillion. Indonesia's economy in the third quarter of 2023 against the previous quarter experienced growth of 1.60 per cent (q-to-q).

In terms of production, the Construction Business Field experienced the highest growth of 5.87 per cent. While from the expenditure side, the Gross Fixed Capital Formation (PMTB) component experienced the highest growth of 7.70 per cent.
Indonesia's economy in the third quarter of 2023 against the third quarter of 2022 grew by 4.94 per cent (y-on-y). In terms of production, the Transportation and Warehousing Business Field experienced the highest growth of 14.74 per cent. In terms of expenditure, the Consumption Expenditure Component of Non-Profit Institutions Serving Households (PK-LNPRT) experienced the highest growth of 6.21 per cent.
As of Q3-2023, Indonesia's economy grew by 5.05 per cent (c-to-c). In terms of production, the largest growth occurred in the Transportation and Warehousing Business Field at 15.30 per cent. Meanwhile, from the expenditure side, the largest growth occurred in the PK-LNPRT Component by 7.01 per cent.


Leading sectors of the Indonesian economy such as Manufacturing Industry, Agriculture, Trade, Mining, and Construction continue to grow.
The three business sectors with the highest growth were Transportation & Warehousing, Other Services, and Accommodation & Eating & Drinking.
In terms of business (production), economic growth was driven by, among others, increased production activities, community mobility, foreign tourist visits, the holding of several national and international events.

Inflation
In October 2023 there was year on year (y-on-y) inflation of 2.56 per cent with a Consumer Price Index (CPI) of 115.64.
Y-on-y inflation occurred due to an increase in prices as indicated by the increase in all expenditure group indices, namely: food, beverages and tobacco group by 5.41 per cent; clothing and footwear group by 0.85 per cent; housing, water, electricity and household fuel group by 1.16 per cent; household supplies, equipment and routine maintenance group by 1.89 per cent; health group by 2.04 per cent; transportation group by 1.20 per cent; information, communication, and financial services group by 0.11 per cent; recreation, sports, and culture group by 1.50 per cent; education group by 1.99 per cent; food and beverage supply/restaurant group by 2.21 per cent; and personal care and other services group by 3.67 per cent.
The month to month (m-to-m) inflation rate for October 2023 was 0.17 per cent and the year to date (y-to-d) inflation rate for October 2023 was 1.80 per cent.
The October 2023 core component y-on-y inflation rate was 1.91 per cent, m-to-m inflation was 0.08 per cent, and y-to-d inflation was 1.54 per cent.

In October 2023, the y-on-y inflation rate was 2.56 per cent and the y-to-d inflation rate was 1.80 per cent. The y-on-y inflation rates for October 2022 and October 2021 were 5.71 per cent and 1.66 per cent, respectively. Meanwhile, the y-to-d inflation rates for October 2022 and October 2021 were 4.73 per cent and 0.93 per cent, respectively.
Exports and Imports in December 2023



A. Export Development
B. Import Development

Indonesia's economy in 2022 grew by 5.31 per cent, higher than the achievement in 2021 which experienced growth of 3.70 per cent. In terms of production, the highest growth occurred in the Transportation and Warehousing Business Field at 19.87 per cent. Meanwhile, from the expenditure side, the highest growth was achieved by the Export of Goods and Services Component by 16.28 per cent.
Indonesia's economy in 2022, calculated based on Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at current prices, reached Rp19,588.4 trillion and GDP per capita reached Rp71.0 million or US$4,783.9.

GDP by Business Field
Growth occurred in all business fields. The business sector that experienced the highest growth was Transportation and Warehousing at 19.87 per cent, followed by Accommodation and Drinking Food Provision at 11.97 per cent, and Other Services at 9.47 per cent. Meanwhile, the Processing Industry, which has a dominant role, grew by 4.89 per cent. Meanwhile, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries and Wholesale and Retail Trade; Car and Motorcycle Repair grew by 2.25 per cent and 5.52 per cent respectively.


Leading Export Commodities:

National Economy
Regional Economy
National Economy
Regional Economy